There are two types of networks from which you can choose for your home network: client/server or workgroup. The type you choose depends on your networking goals, the equipment you want to install, your experience level, and the time you plan to invest. Each method of networking provides distinct advantages and disadvantages. If this is your first network or if you want only a small and simple network, you will most likely set up a workgroup network to start.
A workgroup network is simpler to operate and less expensive than a client/server network. After you gain experience, however, you may want to switch over to a client/server network, using your workgroup setup as a foundation.
Workgroup networking is the most simple and inexpensive network to set up. Network administration is easy, as well, with workgroup networking. Client/server networking, the alternative to workgroup networking, creates more work, more expense, and more administration time. Using a workgroup network In a workgroup network, all computers share their resources—including files, folders, drives, printers, and so on—with all others on the network. Each PC still runs its own local applications and programs.
A workgroup network usually contains from two to ten computers cabled together. You could possibly include more than ten computers, with the right hardware and software; however, when you have more than ten computers on a workgroup network, you slow down the performance of every computer on the network, as well as limit network speed, security, and efficiency. You can use devices, such as routers and switches, to connect more than ten computers efficiently; however, remember that the more computers on your network, the more management, time, and money it will involve.
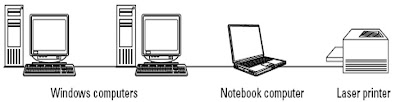 This figure illustrates one example of a workgroup network. Although these computers appear to be beside each other, each one could be located in a different room in a house. The Windows computers, the notebook computer, and the laser printer are all connected; the computers share all resources equally
This figure illustrates one example of a workgroup network. Although these computers appear to be beside each other, each one could be located in a different room in a house. The Windows computers, the notebook computer, and the laser printer are all connected; the computers share all resources equally
A workgroup network is simpler to operate and less expensive than a client/server network. After you gain experience, however, you may want to switch over to a client/server network, using your workgroup setup as a foundation.
Workgroup networking is the most simple and inexpensive network to set up. Network administration is easy, as well, with workgroup networking. Client/server networking, the alternative to workgroup networking, creates more work, more expense, and more administration time. Using a workgroup network In a workgroup network, all computers share their resources—including files, folders, drives, printers, and so on—with all others on the network. Each PC still runs its own local applications and programs.
A workgroup network usually contains from two to ten computers cabled together. You could possibly include more than ten computers, with the right hardware and software; however, when you have more than ten computers on a workgroup network, you slow down the performance of every computer on the network, as well as limit network speed, security, and efficiency. You can use devices, such as routers and switches, to connect more than ten computers efficiently; however, remember that the more computers on your network, the more management, time, and money it will involve.
 This figure illustrates one example of a workgroup network. Although these computers appear to be beside each other, each one could be located in a different room in a house. The Windows computers, the notebook computer, and the laser printer are all connected; the computers share all resources equally
This figure illustrates one example of a workgroup network. Although these computers appear to be beside each other, each one could be located in a different room in a house. The Windows computers, the notebook computer, and the laser printer are all connected; the computers share all resources equally 




0 comments on Understanding Network Types :
Post a Comment